- 408-924-7560
- mineta-institute@sjsu.edu
- Donate
Detecting Drowsy Drivers with Data Fusion Tech
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), there were 91,000 police-reported crashes involving drowsy drivers in 2017 alone—and some estimates claim as many as 6,000 fatal crashes each year may be caused by drowsy drivers. New Mineta Transportation Institute (MTI) research, Detecting Driver Drowsiness with Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Combined with Machine Learning, provides a working prototype of technology to detect drowsy driving and help save lives. By integrating two modes of visual surveillance to examine a biometric expression of drowsiness, including increased eye blinks and yawns, the system can detect when a driver may be dozing off—a technology that could be implemented to save lives in the near future.
The developed system is composed of a webcam and a micro-Doppler radar for data collection and training. After training of the machine learning models, the system is deployed for real-time experimentation in a vehicle, which showed:
- Overall, the system can count the number of eye blinks performed within a minute, number of yawns, and detect head drops, to evaluate if the driver is drowsy or not.
- The experimental results reveal the system can detect the status of a drowsy driver with an average accuracy slightly above 95%.
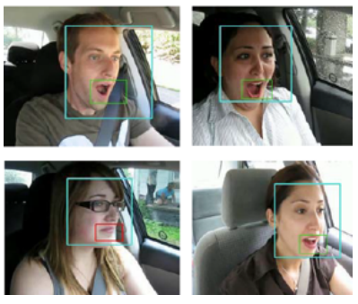
“The dataset used for the blink detection model was a combination of the Closed Eyes in the Wild (CEW) dataset and our own collected images. The CEW dataset consisted of over 2400 subjects with different ethnic backgrounds, various age groups and genders as well as those with and without glasses. Our system is founded on a detailed dataset with three types of classification types and a total of 1728 images,” explains the study’s author.
This on-board system, that monitors a driver’s state of alertness in real-time, could lead to new Artificial Intelligent-based application tools for drivers that could potentially save lives. Future intelligent vehicles can deploy the proposed system to provide additional safety features in case a driver falls asleep while driving.
ABOUT THE MINETA TRANSPORTATION INSTITUTE
At the Mineta Transportation Institute (MTI) at San Jose State University (SJSU) our mission is to increase mobility for all by improving the safety, efficiency, accessibility, and convenience of our nations’ transportation system. Through research, education, workforce development and technology transfer, we help create a connected world. Founded in 1991, MTI is funded through the US Departments of Transportation and Homeland Security, the California Department of Transportation, and public and private grants, including those made available by the Road Repair and Accountability Act of 2017 (SB1). MTI is affiliated with SJSU’s Lucas College and Graduate School of Business.
ABOUT THE AUTHORS
Dr. Hovannes Kulhandjian completed this project as part of the California State University Transportation Consortium (CSUTC). He is an Associate Professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at California State University, Fresno. His current research interests are in applied machine learning, wireless communications, and networking with applications to Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS).
Media Contact:
Irma Garcia,
MTI Communications and Operations Manager
O: 408-924-7560
-
Contact Us
San José State University One Washington Square, San Jose, CA 95192 Phone: 408-924-7560 Email: mineta-institute@sjsu.edu





